Automated Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) market needs to overcome challenges to reach forecast $3.5bn by 2030
- Market challenges post-Covid – including rising living costs, project delays and bottlenecks – will need to be overcome in order for the sector to flourish.
- Opportunities for the automated Micro-Fulfillment Center (MFC) market are growing substantially over time due to the rising demand for shorter delivery times.
- Providing vendors address the barriers to adoption, the MFC market is projected to grow at a CAGR of 65% from 2023 to 2030, reaching over $3.5 billion annually by 2030.
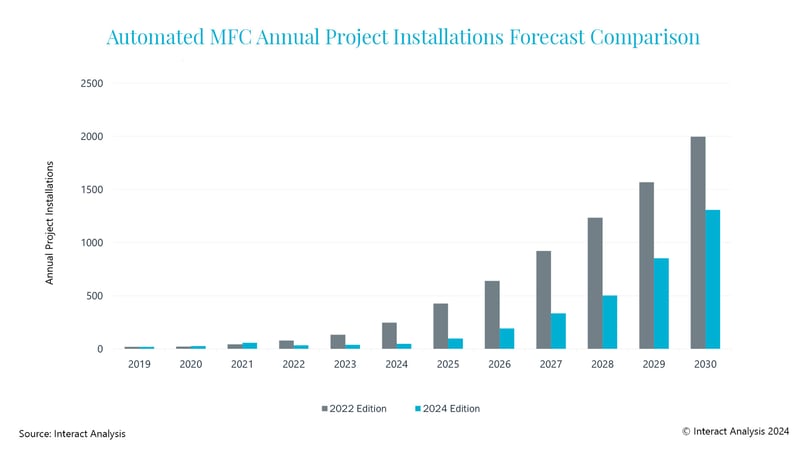
According to the latest report from Interact Analysis, the market for automated micro-fulfillment centers (MFCs) has witnessed a series of challenges to adoption. However, the market opportunity remains high. To reach widespread adoption, several barriers need to be overcome. Assuming these barriers are overcome, Interact Analysis expects the market could grow to an annual revenue of $3.5 billion by 2030.
Nascent stages of growth
Despite initially high expectations, deploying automated MFCs has faced several challenges that fit into two categories: productivity inhibitors and hidden costs.
Productivity inhibitors include integrating manually picked items, with those selected by automation proving inefficient, reducing overall system throughput. Advancements in manual in-store fulfillment software have also narrowed the ROI gap, diminishing the appeal of automated solutions. Additionally, macroeconomic factors, such as rising living costs, have also encouraged consumers to favor in-store shopping over delivery services, further dampening demand.
Furthermore, hidden costs like construction delays and process refinements – along with productivity inhibitors like bottlenecks in the consolidation of manually picked items and MFC replenishment – have also negatively impacted ROI, making the adoption of automated MFCs less attractive.
These barriers to adoption must first be addressed. If they aren’t, the number of MFC deployments will be lower than expected.
Addressing the barriers to adoption
As part of the research process, Interact Analysis identified several key strategies MFC vendors should adopt to address the previously mentioned barriers to adoption. These include sophisticated fulfillment software, flexible and scalable automation solutions, effective pricing models, and many others.
To address the barriers to adoption discussed above, vendors must be able to provide expansive fulfillment software. Online grocery fulfillment is complex and involves the processing of orders, quickly. Automated MFC’s offer the capability to integrate hardware, software, and human labor to solve these logistical challenges efficiently.
Flexibility and scalability are also key. Automation solution providers must be able to provide solutions that cater to different facility sizes while ensuring that they enhance the ROI for retailers. The level of complexity of the solutions must also be considered. Retailers want to be able to install the solution without the need to spend time and money training workers. Many automation providers have successfully done this by having user-friendly interfaces installed on the technology.
What does the future hold for MFCs?
Overall, the market for Automated Micro-Fulfillment Centers (MFCs) is projected to experience significant growth, with a forecast compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 65% from 2023 to 2030, reaching a market size exceeding $3.5 billion annually by 2030.
In 2024 alone, Interact Analysis predicts that grocers will spend $18.5 billion on store labor for online order picking. By comparison, the total warehousing sector will spend ~$180 billion on labor, meaning that grocery in-store fulfillment labor cost equates to 10% of the total warehouse labor costs.
The market is witnessing a bifurcation, with smaller sites for convenience orders and larger sites for weekly shop orders. As a result, technologies such as mobile AS/RS, shuttle AS/RS, and ultra-high-density storage systems are expected to play a significant role in fulfilling weekly shop orders, while nanofulfillment solutions are primarily going to be used in the fulfillment of convenience orders.
Labor is generally still being used for manual in-store picking but the total addressable market for MFCs through localized fulfillment is increasing. Overall, the e-commerce market value for localized fulfillment is expected to increase from $1.9bn in 2023 to $4.4bn in 2030. This is mainly driven by the grocery segment but also other verticals such as healthcare and general merchandise due to the demand for shorter delivery times.
Rowan Stott, Research Analyst at Interact Analysis, comments: “The market is in its early stages of growth, with several barriers to adoption in the MFC industry that haven’t been addressed yet by vendors. We believe that addressing these will be the most important factor in determining future growth.
“Overall, the automated MFC market is poised for substantial growth, driven by the increasing demand for localized fulfillment and advancements in automation technologies. As major retailers continue to invest in these solutions, the market is set to rapidly expand, offering significant opportunities for vendors and stakeholders in the industry.”
About the report
Over the years, we’ve developed and refined our view of what micro-fulfillment is and how to define it. We’ve come to the conclusion that micro-fulfillment is less about the size of the facility, but rather more about the radius of delivery. As such, the scope of this report is constrained by delivery radius, rather than facility size.
In addition to providing a wealth of granular market data, this report will also explore what the biggest barriers limiting the uptake of micro-fulfillment centers, along with the key attributes that retailers are looking for when selecting an automation partner.









